Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) refers to the amount of oxidant consumed under specific conditions when a strong oxidizing agent is used to treat a water sample, expressed in milligrams of oxygen per liter (mg/L).
COD reflects the degree of contamination by reducing substances in water. These reducing substances include organic matter, nitrites, ferrous salts, sulfides, etc. It is one of the indicators of the relative content of organic matter in water.
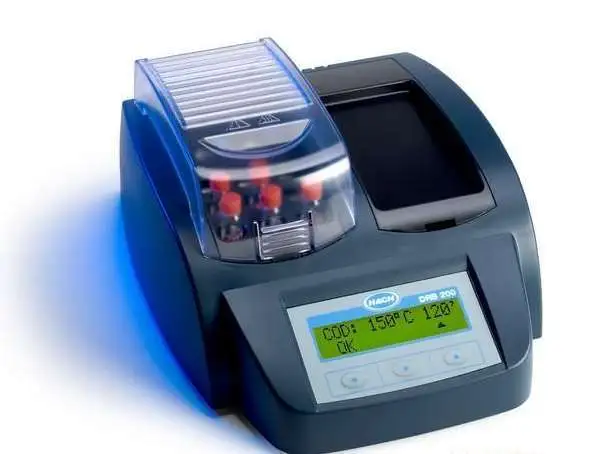

?Potassium Dichromate Method::
1. Principle
In a strongly acidic solution, a measured amount of potassium dichromate oxidizes the reducing substances (e.g., organic matter) in the water sample, with Ag+acting as a catalyst. The excess potassium dichromate is back-titrated with a ferrous ammonium sulfate solution using ferroin as an indicator. The oxygen demand of the reducing substances in the water sample is calculated based on the volume of titrant used.
2. Interferences and Elimination
Chloride ions can be oxidized by dichromate and react with silver sulfate to form precipitates, interfering with the results. Therefore, mercuric sulfate is added to the water sample before reflux to form a complex and eliminate chloride interference.
3. Apparatus
(1) ?Reflux setup?: A full-glass reflux apparatus with a 250 mL conical flask, including: ground-glass conical flask, condenser, electric stove or hot plate, and rubber tubing.
(2) ?50 mL acid burette?.
. Reagents
(1) ?Potassium dichromate solution (1/6 K2Cr2O7= 0.2500 mol/L)?: Dissolve 12.258 g of pre-dried (120°C for 2 hours) primary standard or analytical-grade potassium dichromate in water. Transfer to a 1000 mL volumetric flask and dilute to the mark.
(2) ?Ferroin indicator solution?: Dissolve 1.485 g of 1,10-phenanthroline (C12H8N2.H2O) and 0.695 g of ferrous sulfate in water. Dilute to 100 mL and store in a brown bottle.
(3) ?Ferrous ammonium sulfate standard solution [(NH4)2Fe(SO4)2.6H2O ≈ 0.1 mol/L]?: Dissolve 39.5 g of ferrous ammonium sulfate in water. Slowly add 20 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid while stirring. Cool, transfer to a 1000 mL volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark. Standardize against potassium dichromate before use.
?Standardization Method?:
Pipette 10.00 mL of potassium dichromate standard solution into a 250 mL conical flask. Dilute to ~110 mL with water. Slowly add 30 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid and mix. After cooling, add 3 drops of ferroin indicator and titrate with ferrous ammonium sulfate solution until the color changes from yellow through blue-green to reddish-brown.
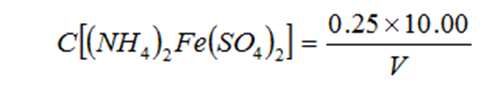
C = Concentration of ferrous ammonium sulfate solution (mol/L)
V = Volume of ferrous ammonium sulfate solution consumed (mL)
(4) ?Sulfuric acid-silver sulfate solution?: Add 5 g of silver sulfate to 500 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid. Allow to stand for 1–2 days to dissolve.
(5) ?Mercuric sulfate?: Crystalline or powdered.
4. Procedure
(1) Add 20 mL of homogenized water sample to the reflux conical flask.
(2) Add ~0.4 g of mercuric sulfate.
(3) Precisely add 10.00 mL of potassium dichromate standard solution and a few glass beads.
(4) Slowly add 30 mL of sulfuric acid-silver sulfate solution.
(5) Mix well, connect the condenser, and reflux for 2 hours.
(6) After cooling, add 90 mL of distilled water through the condenser.
(7) Remove the flask, add 3 drops of ferroin indicator, and titrate with ferrous ammonium sulfate solution until the color changes from yellow through blue-green to reddish-brown. Record the volume consumed.

5. Notes
(1) Add glass beads before adding H2SO4-AgSO4to prevent bumping.
(2) Report COD results with three significant figures.
(3) For COD > 500 mg/L, dilute the sample as follows:
| COD Range | 800 | 1500-2500 | 3000-15000 | >20000 |
| Dilution Factor | 2 | 3-6 | 10-50 | >100 |
Note: The above dilution factors are for reference only.
(4) Check reagent quality and technique using potassium hydrogen phthalate (6H4HP) standard solution. KHP has a theoretical COD of 1.176 g/g. Dissolve 0.4251 g of dried KHP in distilled water and dilute to 1000 mL to prepare a 500 mg/L COD?? standard solution.
(5) A COD thermostatic heater may replace the reflux setup, using air cooling instead of water cooling.
(6) COD rapid testers (colorimetric methods) may also be used.
(7) ?Nitrite interference (20–80 mg/L)?: Research shows that sulfamic acid or ammonium sulfamate can eliminate nitrite interference by reacting as follows:
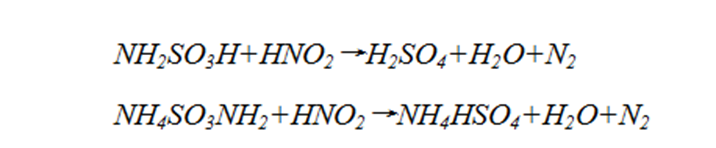
Approximately 10 mg of masking agent is required per 1 mg of NO2–.
Masking agents have minimal impact on blanks below 15 mg2–but significantly affect results above 15 mg.
The above guidelines are for reference only.


 蘇公網(wǎng)安備 32050902101529號(hào)
蘇公網(wǎng)安備 32050902101529號(hào) ?Scan WeChat QR to Follow
?Scan WeChat QR to Follow
